Hace un par de semanas, comenzamos a hablar sobre proyectos que se convirtieron en ganadores de la Escuela de Programación Práctica y Análisis de Datos de la Escuela Superior de Economía - San Petersburgo y JetBrains.
El segundo lugar lo ocupó un equipo de estudiantes de undécimo grado del MSU SSCC. Los chicos implementaron un modelo que predice la solubilidad de sustancias basándose en la representación de moléculas SMILES. Qué es, qué métodos de aprendizaje automático se pueden utilizar en esta tarea, y si los resultados obtenidos concuerdan con experimentos químicos reales, comentaron los autores del proyecto en este post.

Equipo
Nuestro equipo tenía cuatro miembros: Andrey Shandybin, Artyom Vlasov, Vladimir Sverdlov y Zakhar Kravchuk. Todos nosotros este año nos graduamos de SSC MSU y ya teníamos experiencia en aprendizaje automático en un curso especial de ML en SSC y en proyectos paralelos. Nuestra curadora fue Alisa Alenicheva , investigadora del laboratorio de investigación de aplicaciones de aprendizaje automático y aprendizaje profundo JetBrains.
Formulación del problema
, . . , , SMILES ( ) . .
, , — . Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), :
:
baseline ;
(GCN);
;
.
ESOL , 1128 . SMILES. , , - .
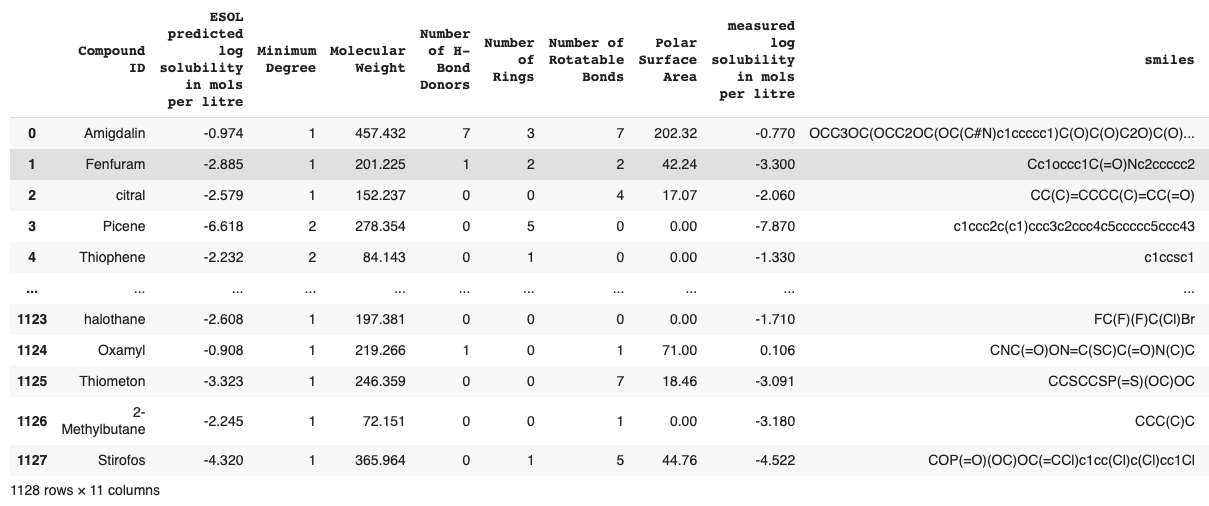
, SMILES. SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System) — ASCII. open-source RDKit SMILES .
class DatasetsHolder:
@staticmethod
def read_datasets(inp_folder_path):
df = pd.read_csv(inp_folder_path)
return df
# return pandas DataFrame
class StandardizeDatasets:
@staticmethod
def standardize_smiles(smi: str) -> Optional[str]:
mol = Chem.MolFromSmiles(smi)
mol = Chem.MolToSmiles(mol)
return mol
"crete typical standardization of one smiles"
@logger.catch()
def standardize(self, inp_path: Path, out_path: Path):
df_reader = DatasetsHolder()
df = df_reader.read_datasets(inp_path)
with Pool(10) as pool:
df['standardize_smiles'] = list(
tqdm(pool.imap(self.standardize_smiles, df.smiles), total=df.shape[0])
)
df.to_csv(out_path, index=False)
return df
"apply standardization to all smiles"
class StandardizeTautomers(StandardizeDatasets):
@staticmethod
def standardize_smiles(smi: str) -> Optional[str]:
Canonicalizer = TautomerCanonicalizer()
mol = Chem.MolFromSmiles(smi)
standorized = Canonicalizer.canonicalize(mol)
return Chem.MolToSmiles(standorized)
# "apply TautomerCanonicalizer() to standardization"
Baseline
baseline- (XGBoost). , , SMILES.
from descriptastorus.descriptors import rdDescriptors
from rdkit import Chem
import logging
from descriptastorus.descriptors import rdNormalizedDescriptors
generator = rdNormalizedDescriptors.RDKit2DNormalized()
def rdkit_2d_features(smiles: str):
features = generator.process(smiles)
if features[0] == False:
print(f'{smiles} were not processed correctly')
return None
else:
return features[1:]
def create_feature_dataframe(df):
feature_names = [x[0] for x in generator.columns]
rdkit_feats = [ ]
for i in range(len(df)):
smiles = df.iloc[i][SMILES_COLUMN]
target_value = df.iloc[i]['measured log solubility in mols per litre']
features = generator.process(smiles)
dictionary = dict(zip(feature_names, features[1:]))
dictionary['target'] = target_value
rdkit_feats.append(dictionary)
return pd.DataFrame(rdkit_feats)
, , , , ( ).
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
X_train = train_data.drop(columns=['target'])
y_train = train_data['target']
X_test = test_data.drop(columns=['target'])
y_test = test_data['target']
model = XGBRegressor()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
, . SMILES . , , — . : , , , , , , .
RDkit
def get_atom_features(mol):
atomic_number = []
num_hs = []
degrees = []
charges = []
tags = []
hybridizations = []
aromatic = []
mass = []
for atom in mol.GetAtoms():
atomic_number.append(atom.GetAtomicNum()) # atomic number
num_hs.append(atom.GetTotalNumHs(includeNeighbors=True)) # number of H in atom
degrees.append(atom.GetTotalDegree()) # total Degree of atom
charges.append(atom.GetFormalCharge()) # Charge of atom
tags.append(int(atom.GetChiralTag())) # chiral tag
hybridizations.append(int(atom.GetHybridization())) # hybridization of atom
if atom.GetIsAromatic(): # Is aromatic of not
aromatic.append(1)
else:
aromatic.append(0)
mass.append(atom.GetMass() * 0.01) # mass
return torch.tensor([atomic_number, num_hs, degrees, charges, tags, hybridizations, aromatic, mass]).t()
def get_edge_index(mol):
row, col = [], []
for bond in mol.GetBonds():
start, end = bond.GetBeginAtomIdx(), bond.GetEndAtomIdx()
row += [start, end]
col += [end, start]
return torch.tensor([row, col], dtype=torch.long)
Fingerprints
? — , , — , . .
Morgan Fingerprints VS Neural Fingerprints
— , -.
. -, , - . -, , , . Neural Fingerprint. , . , .
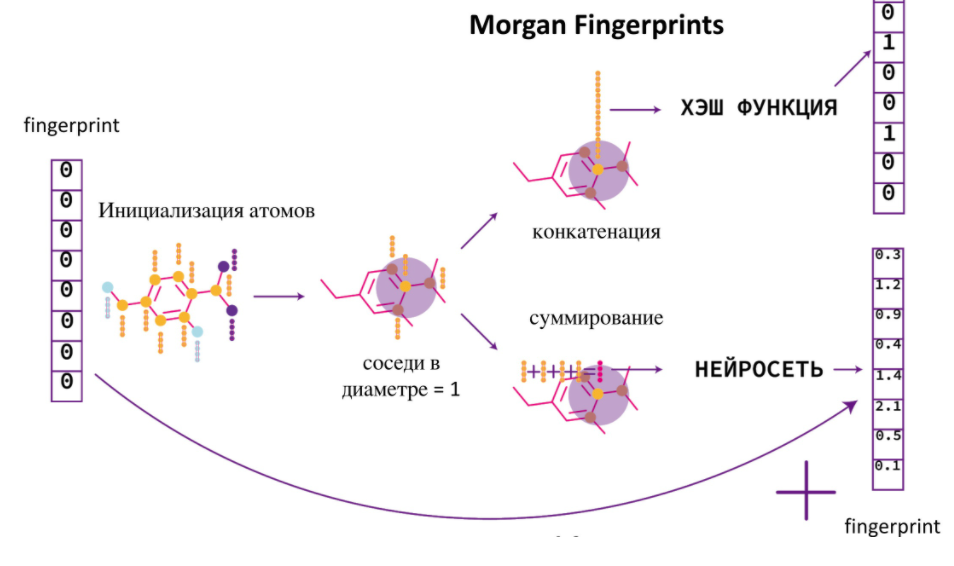
Message passing
. Message passing.
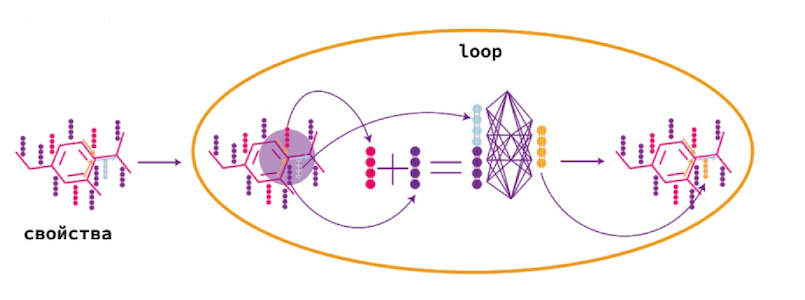
Message passing — , . .
, , . .
PyTorch Geometric.
Message Passing
class GCNConv(MessagePassing):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(GCNConv, self).__init__(aggr='add') # "Add" aggregation (Step 5).
self.lin = torch.nn.Linear(in_channels, out_channels)
def forward(self, x, edge_index):
# x has shape [N, in_channels]
# edge_index has shape [2, E]
# Step 1: Add self-loops to the adjacency matrix.
edge_index, _ = add_self_loops(edge_index, num_nodes=x.size(0))
# Step 2: Linearly transform node feature matrix.
x = self.lin(x)
# Step 3: Compute normalization.
row, col = edge_index
deg = degree(col, x.size(0), dtype=x.dtype)
deg_inv_sqrt = deg.pow(-0.5)
norm = deg_inv_sqrt[row] * deg_inv_sqrt[col]
# Step 4-5: Start propagating messages.
return self.propagate(edge_index, x=x, norm=norm)
def message(self, x_j, norm):
# x_j has shape [E, out_channels]
# Step 4: Normalize node features.
return norm.view(-1, 1) * x_j
Neural loop
class NeuralFP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, atom_features=52, fp_size=50):
super(NeuralFP, self).__init__()
self.atom_features = atom_features
self.fp_size = fp_size
self.loop1 = GCNConv(atom_features, fp_size)
self.loops = nn.ModuleList([self.loop1])
def forward(self, data):
fingerprint = torch.zeros((data.batch.shape[0], self.fp_size), dtype=torch.float).to(device)
out = data.x
for idx, loop in enumerate(self.loops):
updated_fingerprint = loop(out, data.edge_index)
fingerprint += updated_fingerprint
return scatter_add(fingerprint, data.batch, dim=0)
— GCN (Graph Convolutional Network)
, . .
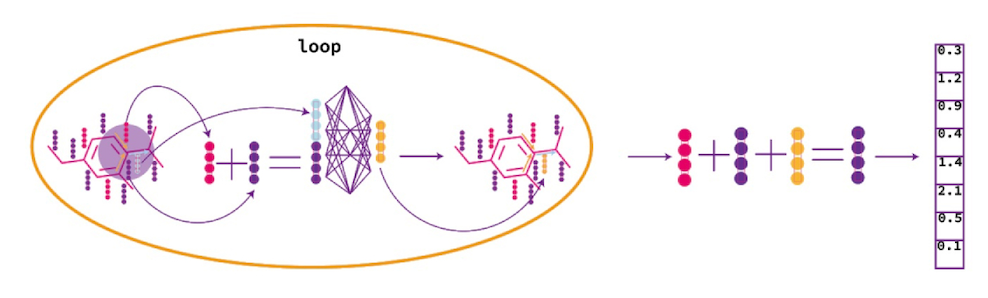
, .
import torch.nn.functional as F
class MLP_Regressor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, neural_fp, atom_features=2, fp_size=50, hidden_size=100):
super(MLP_Regressor, self).__init__()
self.neural_fp = neural_fp
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(fp_size , hidden_size)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
def forward(self, batch):
fp = self.neural_fp(batch)
hidden = self.dropout(self.lin1(fp))
out = self.leakyrelu(self.lin2(hidden))
return out
, .
, GCN SMILES, . , . 200 , . .
MLP regressor
class MLP_Regressor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, neural_fp, atom_features=2, fp_size=100, hidden_size=300, num_additional_features = 207):
super(MLP_Regressor, self).__init__()
self.neural_fp = neural_fp
self.lin1 = nn.Linear(fp_size+num_additional_features, hidden_size)
self.leakyrelu = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
self.lin2 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.2)
def forward(self, batch, additional_features):
fp = self.neural_fp(batch)
fp = torch.cat((fp, additional_features), dim=1)
hidden = self.dropout(self.lin1(fp))
out = self.leakyrelu(self.lin2(hidden))
return out
, , , .
10% , — 90%. . , — RMSE.
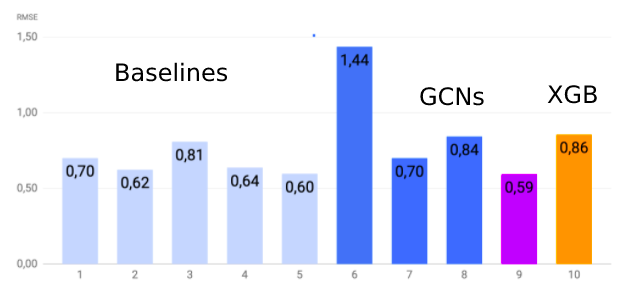
, , - . , , .

, . , : , , - , . , .
, , . Directed Message Passing (DMPNN), Message Passing. , DMPNN, . DMPNN.
. , ESOL, , — , . .
. , .
, , .
: