En lugar de presentar
En primer lugar, me gustaría expresar mi gratitud a todos los que respondieron al primer artículo sobre la optimización del código en C / C ++ utilizando el ejemplo de una función para calcular la raíz cuadrada de un número entero redondeado al número entero más cercano. Gracias a la atención de expertos, se ha corregido un error tipográfico en el texto; la alcancía de algoritmos efectivos se ha repuesto.
Un algoritmo interesante es sqrxi32 de @ Sdima1357 - Ejemplo 1, en lo sucesivo denominado "_i32" para abreviar. El algoritmo "_i32" cumple incondicionalmente la condición de la tarea principal - "redondeo al número entero más cercano" - en todo el conjunto de valores de argumento [0 .. 0xFFFFFFFF], al tiempo que muestra un alto rendimiento.
Ejemplo 1: cálculo de la raíz cuadrada de un número entero, redondeado al número entero más cercano.
uint16_t sqrxi32( uint32_t y )
{
if ( y == 1 )
return 1;
uint32_t xh = y > 0x10000ul ? 0x10000ul : y;
uint32_t xl = 0;
uint32_t xc;
for ( int k = 0; k < 16; k++ )
{
xc = ( xh + xl ) >> 1ul;
if ( xc * xc - xc >= y )
{
xh = xc;
}
else
{
xl = xc;
}
}
return ( xh + xl ) >> 1ul;
}
Otra buena cualidad del algoritmo "_i32" es su predictibilidad temporal. El tiempo de ejecución "_i32" es constante, en contraste con el algoritmo "_evn", que consume tiempo de la máquina en proporción al módulo del argumento.
De Que Trata Este Texto
Observe el efecto complejo de la configuración de compilación y la plataforma de hardware de destino en el rendimiento final, cuando se aplica al mismo código fuente.
El código fuente contiene una solución a un problema con diferentes algoritmos.
.
:
— 3 ;
— 3
:
( main.c)
-
: CubeIDE ( Eclipce CDT)
RELEASE CubeIDE
: «ISO C11 + gnu extensions» (-std=gnu11)
:
CubeMX — default settings, +48MHz, +USART1, +HAL;
Runtime lib: Reduced C ( --spec=nano.specs );
Use float with printf from new lib nano ( -u _printf_float );
1:

2:

3:
FPU «M4» sqrt_fps, (float), «_fps» (Float Point Short) — 2.
2: float
uint16_t sqrt_fps( uint32_t number )
{
if ( number < 2 )
return (uint16_t) number;
float f_rslt = sqrtf( number );
uint32_t rslt = (uint32_t) f_rslt;
if ( !( f_rslt - (float) rslt < .5 ) )
rslt++;
return (uint16_t) rslt;
}
«_fps» 22- , 1E+5 — 1.
1: "_fps" 1E+6+

[0 .. 1E+5].
4:
— , .
, «x86» «ARM Cortex» . — 2.
2:
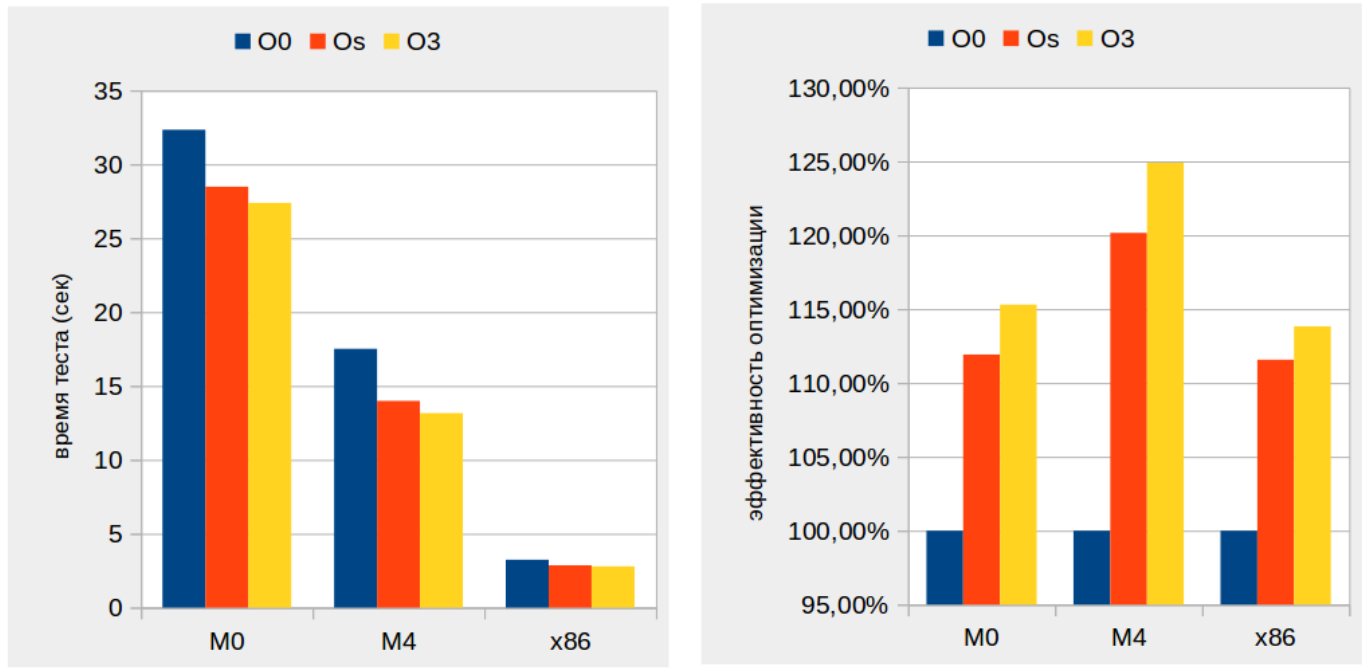
Y ( 4), . X — .
( 2), , .
, , , : -O0, -Os, -O3.
( 2) : -O0, -Os, -O3.
100% , ( -O0 ). .
( ‑O0 ) , - .
«M4».
x86
( 3) Y . X — ( 4).
, .
X . .
3: x86

«x86» .
.
( ‑O0 ) 39% «_fpu» ( ‑Os ) 16% «_fps» ( ‑O3 ). , «x86» .
, -O3 -Os.
M4
«M4» ( 4).
4: M4

«M4» «_fps», — float.
FPU «M4» — 5.
, «_fps» 1E+5 (. 1) , FPU «M4» .
5: M4 FPU
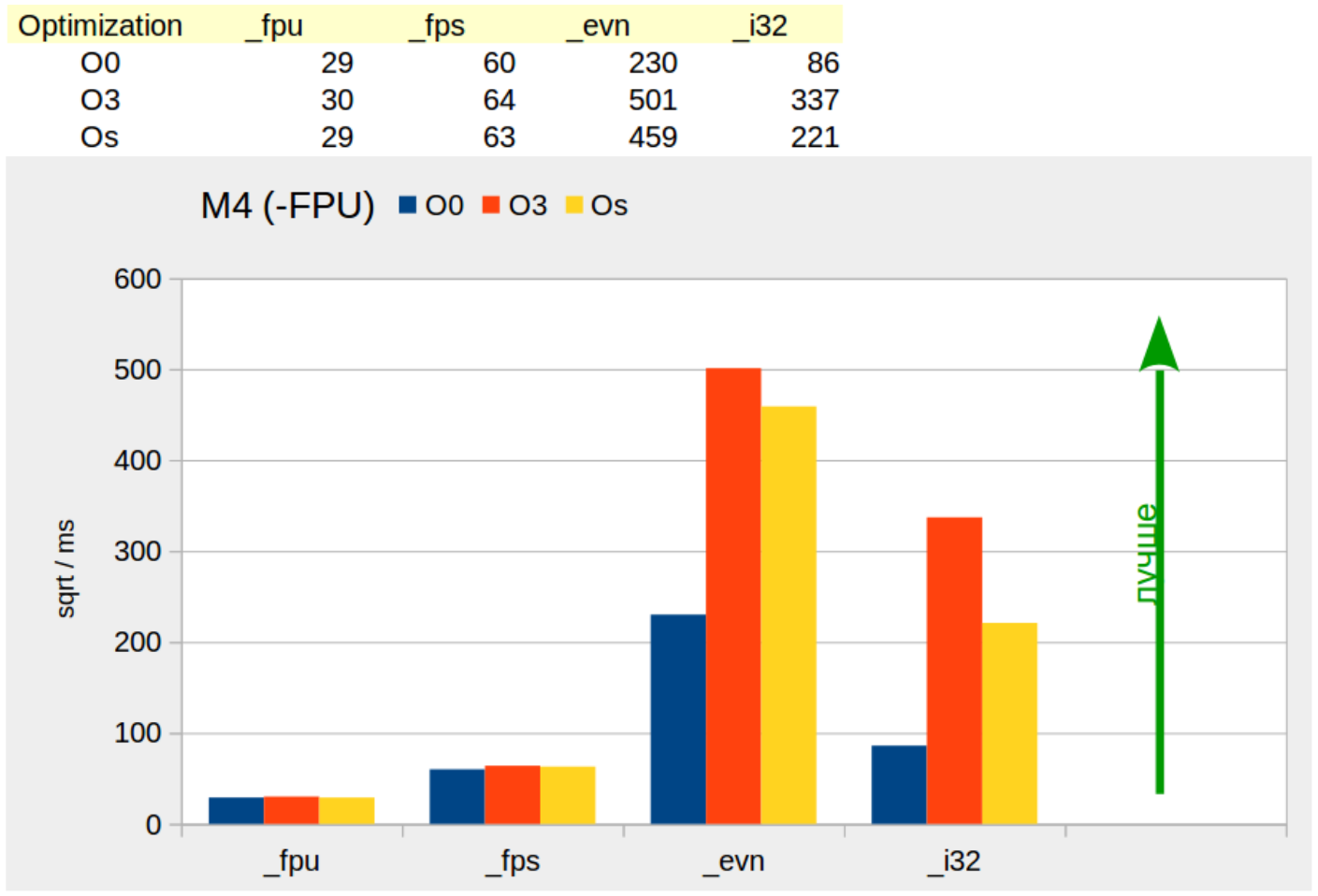
M0
«M0» «M4» FPU ( 5), — 6.
, «M4», «M0» — 48 MHz. , «M0» , «M4», .
6: M0
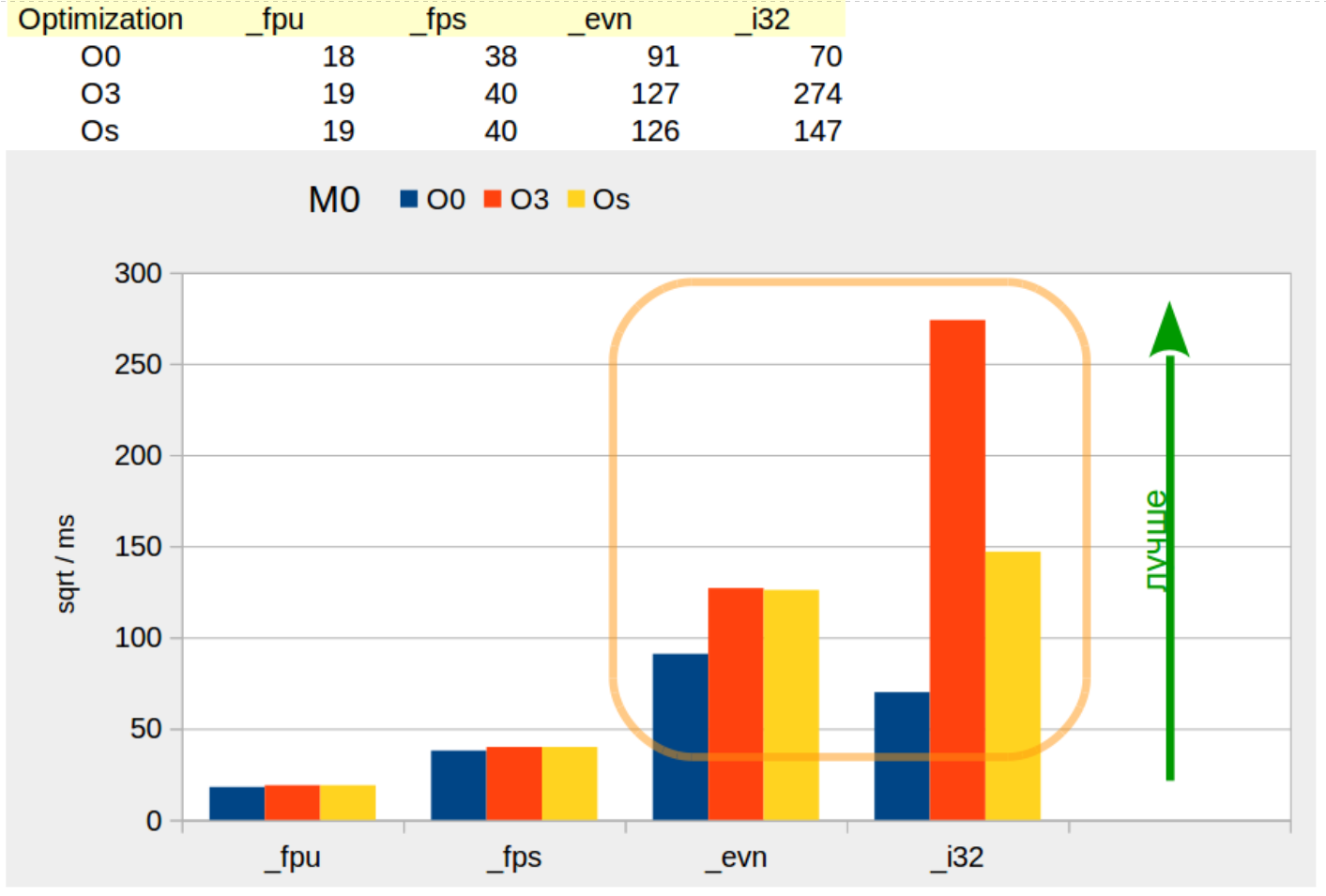
«_fps» «M0» «_fpu».
.
( 6) .
( ‑O0 ) «_evn» «_i32». «_evn» , «_i32», .
. , «M4» «x86» .
.
, , ( 3 6).
.
, , . .
1. x86
CubeIDE (Eclipse CDT) C
— 3
sqrt_cmp.h — 6
:
IDE;
— 4
( -O0, -O3, -Os ) .
3: x86 — main.c
#include "sqrt_cmp.h"
int main( void )
{
main_Of_SqrtComp();
return 0;
}
4 x86
gcc main.c -o main -I. -Wall -lm -std=gnu11 -O3 && ./main
«x86» , main.c sqrt_cmp.h , (pwd).
7: «x86»
2. STM32
CubeIDE STM32 (CubeMX)
sqrt_cmp.h STM32 — 6
sqrt_cmp.h main.c — 5
IDE
Cambiando el tipo de optimización (-O0, -O3, -Os) observe el resultado
Ejemplo 5: código fuente para STM32 (con espacios <...>) - main.c
< … >
/* Private includes ----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include "sqrt_cmp.h"
/* USER CODE END Includes */
< … >
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
< … >
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
main_Of_SqrtComp();
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
Apéndice 3. Procedimiento para probar otros algoritmos y plataformas
El montaje de prueba para otras plataformas se realiza por analogía.
Para plataformas de hardware distintas de las mencionadas anteriormente (Tabla 3), es probable que se requiera una modificación cosmética del archivo "sqrt_cmp.h".
Ejemplo 6: contenido del archivo sqrt_cmp.h
/******************************************************************************
* File: sqrt_cmp.h Created on 5 . 2020 .
* CC0 1.0 Universal (CC0 1.0)
* Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication
* No Copyright
*
* TAB Size .EQ 4
********************************************************************************/
#ifndef __SQRT_CMP_H
#define __SQRT_CMP_H
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/******************************************************************************
* Interface of the entry point for all sqrt tests
******************************************************************************/
void main_Of_SqrtComp();
/******************************************************************************
* test case selection: TEST_SET
* select one of the test suite via a comment.
******************************************************************************/
#define TEST_SET TEST_ALL
//#define TEST_SET TEST_ROUNDING
//#define TEST_SET TEST_PERFORMANCE
/******************************************************************************
* Interfaces of test functions.
* See implementation of them at the end of this file.
******************************************************************************/
typedef uint16_t (*sqrt_func)( uint32_t number );
uint16_t sqrt_fpu( uint32_t number ); // floating point function from article
uint16_t sqrt_evn( uint32_t number ); // integer function from article
uint16_t sqrxi32( uint32_t y ); // integer function from comment by
uint16_t sqrt_fps( uint32_t number ); // optimized floating point function for Cortex M4
// <-- insert interface of your function here
/******************************************************************************
* Set to variable named as 'round_test_func' below
* to the alias of one of the functions above.
* The NULL will select last function in comp_list[]
******************************************************************************/
sqrt_func round_test_func = sqrt_fps; // specific instance for the rounding test
//sqrt_func round_test_func = sqrxi32; // specific instance for the rounding test
//sqrt_func round_test_func = sqrt_evn; // specific instance for the rounding test
//sqrt_func round_test_func = NULL; // last function in comp_list[]
/******************************************************************************
* The array of test functions for competing routines is called comp_list[].
* Adding a new function to the test:
- copy the implementation of the new function to the end of this file;
- declare the function interface at the beginning of this file;
- add the alias and declaration of the new function to
end of array named comp_list[].
******************************************************************************/
// @formatter:off
typedef struct
{
sqrt_func fsqrt;
char * alias;
} SCompFunc;
SCompFunc comp_list[] = // competition list
{
{ sqrt_fpu, "_fpu" },
{ sqrt_fps, "_fps" },
{ sqrt_evn, "_evn" },
{ sqrxi32, "_i32" }
// <-- insert your function name & alias here
};
/* @formatter:on */
/******************************************************************************
* Platform-independent definitions
******************************************************************************/
#define PUT_FORMAT_MSG(f_, ...) { \
sprintf( (char *)s_buf, (char *)f_, ##__VA_ARGS__ ); \
PUT_MSG( (char *)s_buf ); }
#define MS_PER_SEC 1000
#define US_PER_SEC ( MS_PER_SEC * MS_PER_SEC )
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof a / sizeof *a) // size of static array at runtime
#define SIRV(f) if ( f ) ; // suppress Ignore Return Value warning
/******************************************************************************
* Platform-specific defines
******************************************************************************/
#if defined( USE_HAL_DRIVER ) // STM32 ARM Cortex platform
# include <string.h>
# include "main.h"
//*****************************************************************************
// Platform-specific defines for the helper functions
# define SCALE_RATE 1 // must be .GE than 1
# define X_CLOCK HAL_GetTick()
# define X_DELAY( ms ) HAL_Delay( ms )
//*****************************************************************************
// Platform-specific defines for the terminal output
# define USART_HANDLE huart1 // set valid USART handler alias here defined by the config of MCU
# define USART_TIMEOUT 150 // max timeout for HAL_UART_Transmit
extern UART_HandleTypeDef USART_HANDLE;
extern HAL_StatusTypeDef HAL_UART_Transmit ( UART_HandleTypeDef *huart, uint8_t *pData, uint16_t Size, uint32_t Timeout );
# define PUT_MSG( msg ) \
HAL_UART_Transmit( &USART_HANDLE, (uint8_t *)msg, strlen( (char *)msg ), USART_TIMEOUT )
# define CPU_CLOCK_MHz ( SystemCoreClock / US_PER_SEC ) // CPU CLK in MHz
# if defined( STM32F0 )
# define CPU_ID ( "STM32 ARM Cortex M0" )
# elif defined ( STM32F3 )
# define CPU_ID ( "STM32 ARM Cortex M4" )
# else
# define CPU_ID ( "Maybe STM32 ARM Cortex" )
# endif
# define PUT_SYS_INFO PUT_FORMAT_MSG( " %s @ "fdU()" MHz\n", CPU_ID, CPU_CLOCK_MHz )
#else // #if defined( USE_HAL_DRIVER )
# include <time.h>
# include <stdlib.h>
//*****************************************************************************
// Platform-specific defines for the helper functions
# define SCALE_RATE 100 // must be .GE than 1
# define X_CLOCK (uint32_t) x_clock()
# define X_DELAY( ms ) x_delay( ms )
uint32_t x_clock()
{
uint64_t result = (uint64_t) clock();
result *= MS_PER_SEC;
result /= CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
return (uint32_t) result;
}
void x_delay( uint32_t ms )
{
uint64_t tm = x_clock();
while ( ( x_clock() - tm ) < ms )
;
}
//*****************************************************************************
// Platform-specific defines for the terminal output
# define PUT_MSG( msg ) \
printf( "%s", (char *)msg ), fflush ( stdout );
# if defined( __unix__ ) // anybody other platform for gcc
# define PUT_SYS_INFO SIRV( system( "cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep 'model name' | head -1 | sed s/'model name\t:'/''/" ) )
# else
# define PUT_SYS_INFO PUT_MSG( "Undefined System & CPU" )
# endif // # if defined( __unix__ ) // anybody other platform for gcc
#endif // #if defined( USE_HAL_DRIVER )
#if ( __WORDSIZE == 64 )
# define fdI(s) "%" #s "d"
# define fdU(s) "%" #s "u"
# define fdX(s) "%" #s "x"
#else // let's say __WORDSIZE == 32
# define fdI(s) "%" #s "ld"
# define fdU(s) "%" #s "lu"
# define fdX(s) "%" #s "lx"
#endif // #if ( __WORDSIZE == 64 )
#if defined ( DEBUG ) || defined ( _DEBUG ) // chk build mode of CubeIDE
# define BUILD_MODE "DEBUG"
#else // Maybe Release
# define BUILD_MODE "RELEASE"
#endif // #if defined ( DEBUG ) || defined ( _DEBUG )
/******************************************************************************
* the helper data with testing ranges
******************************************************************************/
// @formatter:off
typedef struct
{
uint32_t start;
uint32_t stop;
uint32_t repeat;
} STestRange;
STestRange test_rngs[] =
{
{ 0, 1000, 100 * SCALE_RATE },
{ 0, 10000, 10 * SCALE_RATE },
{ 0, 100000, 1 * SCALE_RATE }
};
uint32_t test_results[ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs )][ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ) + 1];
#define MSG_BUFF_SIZE 512
uint8_t s_buf[MSG_BUFF_SIZE]; // buffer for a terminal output
/* @formatter:on */
/******************************************************************************
* Test sets definitions. Do not change it.
******************************************************************************/
#define TEST_ROUNDING 1
#define TEST_PERFORMANCE 2
#define TEST_ALL ( TEST_ROUNDING | TEST_PERFORMANCE )
#ifndef TEST_SET
# define TEST_SET TEST_ALL
#endif
#define HI_ROUND_TEST_RANGE_END 0x007FFFFFUL
#define HI_ROUND_TEST_RANGE_START ( HI_ROUND_TEST_RANGE_END >> 4 )
/******************************************************************************
* Interface of helper functions
******************************************************************************/
void main_Header();
void testRounding();
void testPerformance();
/******************************************************************************
* Implementation of the entry point for all sqrt tests
******************************************************************************/
void main_Of_SqrtComp()
{
X_DELAY( MS_PER_SEC / 2 ); // suppress the output of a previous instance
// while the new instance is loading into the MCU
uint32_t start_time = X_CLOCK;
main_Header();
// checking normal and extended ranges for rounding
if ( TEST_SET & TEST_ROUNDING )
testRounding();
// checking normal ranges on execution time
if ( TEST_SET & TEST_PERFORMANCE )
testPerformance();
uint32_t test_time = X_CLOCK - start_time;
uint32_t test_m = ( test_time / MS_PER_SEC ) / 60;
uint32_t test_s = ( test_time / MS_PER_SEC ) % 60;
uint32_t test_ms = test_time % MS_PER_SEC;
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\ndone, spent time: "fdU()" m, "fdU()"."fdU()" s\n", test_m, test_s, test_ms );
}
/******************************************************************************
* Implementation of the helper functions
******************************************************************************/
void main_Header()
{
PUT_MSG( "\n\n**********************************************************\n" );
PUT_SYS_INFO;
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "*********** %s, built at %s\n", BUILD_MODE, __TIME__ );
}
void testPerformance()
{
uint32_t i_func, i_rpt, i_rng;
uint32_t number, first, second, diff;
uint64_t temp;
PUT_MSG( "----------+ Performance test" );
for ( i_rng = 0; i_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs ); i_rng++ )
{
PUT_MSG( "\n" );
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "test range:["fdU()".."fdU()"], repeat="fdU()"\n", test_rngs[i_rng].start, test_rngs[i_rng].stop,
test_rngs[i_rng].repeat );
test_results[i_rng][0] = test_rngs[i_rng].stop;
for ( i_func = 0; i_func < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ); i_func++ )
{
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "%s ... ", comp_list[i_func].alias );
first = X_CLOCK;
for ( i_rpt = 0; i_rpt < test_rngs[i_rng].repeat; i_rpt++ )
for ( number = test_rngs[i_rng].start; number < test_rngs[i_rng].stop; number++ )
comp_list[i_func].fsqrt( number );
second = X_CLOCK;
diff = second - first;
temp = ( test_rngs[i_rng].stop - test_rngs[i_rng].start ) * test_rngs[i_rng].repeat;
test_results[i_rng][i_func + 1] = (uint32_t) ( temp / diff );
if ( i_func < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ) - 1 )
PUT_MSG( ", " );
}
}
// small report
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\n----------+ Report: sqrt`s calls per ms\n%10s", "range" );
for ( i_func = 0; i_func < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ); i_func++ )
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "%10s", comp_list[i_func].alias );
for ( i_rng = 0; i_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs ); i_rng++ )
{
PUT_MSG( "\n" );
for ( i_func = 0; i_func < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ) + 1; i_func++ )
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( fdU( 10 ), test_results[i_rng][i_func] );
}
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\n----------+\n%10s", "average" );
for ( i_func = 0; i_func < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ); i_func++ )
{
temp = 0;
for ( i_rng = 0; i_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs ); i_rng++ )
temp += test_results[i_rng][i_func + 1];
temp /= ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs );
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( fdU( 10 ), (uint32_t)temp );
}
}
void testRoundingFunction( uint32_t start, uint32_t finish, sqrt_func psqrt, char *fname );
void testRounding()
{
uint16_t i_rng;
uint16_t f_rng;
PUT_MSG( "----------+ Rounding test\n" );
// checking the existence for the test function
for ( f_rng = 0; f_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ); f_rng++ )
if ( comp_list[f_rng].fsqrt == round_test_func )
break;
if ( !( f_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ) ) )
{
f_rng = ARRAY_SIZE( comp_list ) - 1;
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "Value of 'round_test_func' not found.\n" );
}
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "Function '%s' is tested for rounding.\n", comp_list[f_rng].alias );
// checking standard ranges
for ( i_rng = 0; i_rng < ARRAY_SIZE( test_rngs ); i_rng++ )
testRoundingFunction( test_rngs[i_rng].start, test_rngs[i_rng].stop, comp_list[f_rng].fsqrt, comp_list[f_rng].alias );
// checking extended range
testRoundingFunction( HI_ROUND_TEST_RANGE_START, HI_ROUND_TEST_RANGE_END, comp_list[f_rng].fsqrt, comp_list[f_rng].alias );
}
void turn_the_fan( uint32_t ms );
void testRoundingFunction( uint32_t start, uint32_t finish, sqrt_func psqrt, char *fname )
{
uint32_t rf, ri;
uint32_t n, c = 0;
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "test range:["fdU( 10 )".."fdU( 10 )"] ... ", start, finish );
for ( n = start; n < finish; n++ )
{
rf = sqrt_fpu( n );
ri = ( *psqrt )( n );
if ( rf != ri )
{
if ( c++ > 3 )
{
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\b\n(!)too many mistakes in '%s', ", fname );
break;
}
else
{
double d = sqrt( (double) n );
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\b\n%s("fdU( 10 )")="fdU()" != "fdU(), fname, n, ri, rf );
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( " (real value is %.6lf)", d );
}
}
turn_the_fan( MS_PER_SEC );
}
if ( !c )
{
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\b done.\n" );
}
else
{
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "test failed.\n" );
}
}
void turn_the_fan( uint32_t ms )
{
static char ca[] = "|/-\\";
static uint32_t cs = ARRAY_SIZE(ca) - 1;
static uint32_t cn = 0;
static uint32_t at = 0;
uint32_t ct = X_CLOCK;
if ( ct - at > ms )
{
at = ct;
PUT_FORMAT_MSG( "\b%c", ca[cn++ % cs] );
}
}
/******************************************************************************
* Implementation of the sqrt functions
******************************************************************************/
// floating point arg & result with double
uint16_t sqrt_fpu( uint32_t number )
{
if ( number < 2 )
return (uint16_t) number;
double f_rslt = sqrt( number );
uint32_t rslt = (uint32_t) f_rslt;
if ( !( f_rslt - (double) rslt < .5 ) )
rslt++;
return (uint16_t) rslt;
}
// floating point arg & result with float
uint16_t sqrt_fps( uint32_t number )
{
if ( number < 2 )
return (uint16_t) number;
float f_rslt = sqrtf( number );
uint32_t rslt = (uint32_t) f_rslt;
if ( !( f_rslt - (float) rslt < .5 ) )
rslt++;
return (uint16_t) rslt;
}
// unsigned integer arg & result
// @formatter:off
uint16_t sqrt_evn ( uint32_t number )
{
if ( number < 2 )
return ( uint16_t ) number;
uint32_t temp;
uint32_t div;
uint32_t rslt;
if ( number & 0xFFFF0000L )
if ( number & 0xFF000000L )
if ( number & 0xF0000000L )
if ( number & 0xE0000000L )
div = 43771;
else
div = 22250;
else
if ( number & 0x0C000000L )
div = 11310;
else
div = 5749;
else
if ( number & 0x00F00000L )
if ( number & 0x00C00000L )
div = 2923;
else
div = 1486;
else
if ( number & 0x000C0000L )
div = 755;
else
div = 384;
else
if ( number & 0xFF00L )
if ( number & 0xF000L )
if ( number & 0xC000L )
div = 195;
else
div = 99;
else
if ( number & 0x0C00L )
div = 50;
else
div = 25;
else
if ( number & 0xF0L )
if ( number & 0x80L )
div = 13;
else
div = 7;
else
div = 3;
rslt = number;
while ( 1 )
{
temp = number / div;
temp += div;
div = temp >> 1;
div += temp & 1;
if ( rslt > div )
rslt = div;
else
{
if ( number / rslt == rslt - 1 && number % rslt == 0 )
rslt--;
return ( uint16_t ) rslt;
}
}
}
/* @formatter:on */
// unsigned integer arg & result
uint16_t sqrxi32( uint32_t y )
{
if ( y == 1 )
return 1;
uint32_t xh = y > 0x10000ul ? 0x10000ul : y;
uint32_t xl = 0;
uint32_t xc;
for ( int k = 0; k < 16; k++ )
{
xc = ( xh + xl ) >> 1ul;
if ( xc * xc - xc >= y )
{
xh = xc;
}
else
{
xl = xc;
}
}
return ( xh + xl ) >> 1ul;
}
// <-- insert implementation of your function sqrt here
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif // __SQRT_CMP_H