Vea la publicación anterior aquí .
Prueba de hipótesis estadísticas
Para los estadísticos y científicos de datos, probar una hipótesis estadística es un procedimiento formal. El enfoque estándar para probar una hipótesis estadística implica definir el campo de estudio, decidir qué variables se necesitan para medir el tema y luego proponer dos hipótesis en competencia. Para evitar considerar solo aquellos datos que apoyan nuestras evaluaciones subjetivas, los investigadores establecen claramente su hipótesis por adelantado. Luego, basándose en los datos, aplican estadísticas de muestra para confirmar o rechazar esta hipótesis.
La prueba de hipótesis estadística implica el uso de estadísticas de prueba, es decir, valor de la muestra en función de los resultados de la observación. Una estadística de prueba es un valor calculado a partir de datos de muestra que se utiliza para evaluar la solidez de los datos que confirman una hipótesis estadística nula y se utiliza para identificar una medida de discrepancia entre valores empíricos e hipotéticos. Los métodos de verificación específicos se denominan pruebas, por ejemplo, prueba z, prueba t (respectivamente, prueba z de Fisher, prueba t de Student), etc. dependiendo de las estadísticas de prueba utilizadas en ellos.
Nota . La ciencia estadística nacional utiliza el término "vago" "estadísticas de criterio". Brumoso porque aquí nuevamente observamos una sustitución suave: en lugar de una prueba, surge un criterio. De hecho, un criterio es un principio o una regla. Por ejemplo, al hacer la prueba z, la prueba t, etc., usamos el estadístico z, el estadístico t, etc. en consecuencia. en la regla para rechazar la hipótesis. Esto se resume muy bien en la siguiente tabla:
Probando la hipótesis |
Estadísticas de prueba |
Regla de rechazo de hipótesis |
pruebas z |
estadísticas z |
Si el estadístico de prueba ≥ zo ≤ -z, entonces rechace la hipótesis nula H 0 . |
pruebas t |
t-estadisticas |
Si el estadístico de prueba es ≥ to ≤ -t, entonces rechace la hipótesis nula H 0 . |
Análisis de varianza (ANOVA) |
Estadísticas F |
≥ F, H0. |
- |
- |
≥ χ, H0. |
, -, - . , , -.
, « - »? . , . , , . , , . H0.
, , , , . « » , , -, , , .
, H1. , . , , . , - , :
H0: - -
H1: - -
, - -. «» (.. ), , , . (.. , ), .
, , .
, . , , , .
, :
,
,
, 1- 2- :
|
H0 |
H0 |
H0 |
|
1- ( ) |
H0 |
2- ( ) |
|
1- , 2- . , , , , . , , .
. 5% 1%. 5% , 1% — . α () . , ( -, ), , . , , . 5%, .
-
- AcmeContent , -, . , , - .
, , AcmeContent - . - , 5% -. . . , , "0", ( , ) , "1".
z-
, .
z- . , -, , , .
, . Z- , .. (), . , , , :
σ2a — a, σ2b — b na nb — a b. Python :
def pooled_standard_error(a, b, unbias=False):
''' '''
std1 = a.std(ddof=0) if unbias==False else a.std()
std2 = b.std(ddof=0) if unbias==False else b.std()
x = std1 ** 2 / a.count()
y = std2 ** 2 / b.count()
return sp.sqrt(x + y)
, , . z:
pooled_standard_error
, , z- :
def z_stat(a, b, unbias=False):
return (a.mean() - b.mean()) / pooled_standard_error(a, b, unbias)
z , , . , z- , . , , z- :
def z_test(a, b):
return stats.norm.cdf([ z_stat(a, b) ])
z- -. -, , - . groupby('site')['dwell-time']
. get_group
, -:
def ex_2_14():
'''
- z-'''
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
a = groups.get_group(0)
b = groups.get_group(1)
print('a n: ', a.count())
print('b n: ', b.count())
print('z-:', z_stat(a, b))
print('p-: ', z_test(a, b))
a n: 284
b n: 16
z-: -1.6467438180091214
p-: [0.04980536]
5% 95%. , , 95%- . , , 5%- .
P- — 1- , . p-, , , .
0.0498, 4.98%. 5% , , .
:
H0: - -
H1: - -.
, - .
, - -, — , , . , - 16 . , .
, , .
t-
t- , , , .
1908 , , , . «».
— , t- , . , t- , 1. , , .
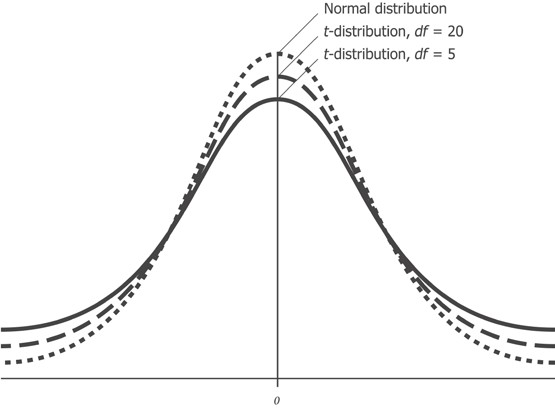
, t- . .
, df . degrees of freedom, . , .
, , , 10 8, , , 12. , , , , .
, , , 10, 10, . , 10, 10, , , .
: , . : .
, .
t-
t- t-. z-, . t- t- :
Sa̅b̅ — . , :
σa σb, . t- ().
, t- :
. , t- . :
def pooled_standard_error_t(a, b):
''' t-'''
return sp.sqrt(standard_error(a) ** 2 +
standard_error(b) ** 2)
t- z- -, :
t_stat = z_stat
def ex_2_15():
''' t-
-'''
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
a = groups.get_group(0)
b = groups.get_group(1)
return t_stat(a, b)
-1.6467438180091214
, — z- , .
t-
t- , p-. t-, t-, :
def t_test(a, b):
df = len(a) + len(b) - 2
return stats.t.sf([ abs(t_stat(a, b)) ], df)
, 298.

, . :
H0:
H1:
:
def ex_2_16():
'''
- t-'''
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
a = groups.get_group(0)
b = groups.get_group(1)
return t_test(a, b)
array([ 0.05033241])
p-, 0.05. α, 5%, , . t- . , z- .
, - . , .
, , , , . «» , α . , , , , .
— . , .
, 1- . , - . α , -.

stats scipy t-. stats.ttest_ind
. - . equal_var
True
, , , ( t_test_verbose
, ( ):
def ex_2_17():
''' t-'''
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
a = groups.get_group(0)
b = groups.get_group(1)
return t_test_verbose(a, sample2=b, fn=stats.ttest_ind) #t-
{'p-': 0.12756432502462475,
' ': 17.761382349686098,
' ': (76.00263198799597, 99.89877646270826),
'n1 ': 284,
'n2 ': 16,
' x ': 87.95070422535211,
' y ': 122.0,
' x ': 10463.941024237296,
' y ': 6669.866666666667,
't-': -1.5985205593851322}
t- t_test_verbose
p-. P- 2 , . , , , , stats t-, t- , , . , , .
t-
t- , , . , , , sciy stats.ttest_1samp
.
. , , - , 90 ., :
def ex_2_18():
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
b = groups.get_group(1)
return t_test_verbose(b, mean=90, fn=stats.ttest_1samp)
{'p- ': 0.13789520958229415,
' df ': 15.0,
' ': (78.4815276659039, 165.5184723340961),
'n1 ': 16,
' x ': 122.0,
' x ': 6669.866666666667,
't- ': 1.5672973291495713}
t_test_verbose
p- , . 78.5 165.5 ., , , 90 . . , .
, t- , , , . resampling. , . , , , , , .
, — . , , , , . , . . , .
, , — , ( ) , « », ( , , .).
pandas sample . , .. n
( , ), axis
(, ) replace
( ), False
. , :
def ex_2_19():
'''
'''
groups = load_data('new-site.tsv').groupby('site')['dwell-time']
b = groups.get_group(1)
xs = [b.sample(len(b), replace=True).mean() for _ in range(1000)]
pd.Series(xs).hist(bins=20)
plt.xlabel(' , .')
plt.ylabel('')
plt.show()
:

, , -. , 16 , ( 78 165 .), t-.
, , . , , .
-. , , .
, - AcmeContent -. , 19 . -, , 20 -, .
- 19 - . , 5% , 24 .
, -. , 0 - , 1 19 :
def ex_2_20():
df = load_data('multiple-sites.tsv')
return df.groupby('site').aggregate(sp.mean)
:
site |
dwell-time |
0 |
79.851064 |
1 |
106.000000 |
2 |
88.229167 |
3 |
97.479167 |
4 |
94.333333 |
5 |
102.333333 |
6 |
144.192982 |
7 |
123.367347 |
8 |
94.346939 |
9 |
89.820000 |
10 |
129.952381 |
11 |
96.982143 |
12 |
80.950820 |
13 |
90.737705 |
14 |
74.764706 |
15 |
119.347826 |
16 |
86.744186 |
17 |
77.891304 |
18 |
94.814815 |
19 |
89.280702 |
-, , - . - , Python itertools, , :
import itertools
def ex_2_21():
''' - t-
" "'''
groups = load_data('multiple-sites.tsv').groupby('site')
alpha = 0.05
pairs = [list(x) # n k
for x in itertools.combinations(range(len(groups)), 2)]
for pair in pairs:
gr, gr2 = groups.get_group( pair[0] ), groups.get_group( pair[1] )
site_a, site_b = pair[0], pair[1]
a, b = gr['dwell-time'], gr2['dwell-time']
p_val = stats.ttest_ind(a, b, equal_var = False).pvalue
if p_val < alpha:
print(' - %i %i : %f'
% (site_a, site_b, p_val))
. , , , . , , - .
, - — , 90 ., -:
def ex_2_22():
groups = load_data('multiple-sites.tsv').groupby('site')
alpha = 0.05
baseline = groups.get_group(0)['dwell-time']
for site_a in range(1, len(groups)):
a = groups.get_group( site_a )['dwell-time']
p_val = stats.ttest_ind(a, baseline, equal_var = False).pvalue
if p_val < alpha:
print(' %i - : %f'
% (site_a, p_val))
-, :
6 - : 0.005534
10 - 10 : 0.006881
p- ( 1%) , . , . t- 20 α, 0.05. α , . 20- t- , - 20.
, t- . . .
, . — , , 1- . .
— α . , k -, α 0.05, :
1- . ex-2-22
, , α :
def ex_2_23():
''' - t-
(0) '''
groups = load_data('multiple-sites.tsv').groupby('site')
alpha = 0.05 / len(groups)
baseline = groups.get_group(0)['dwell-time']
for site_a in range(1, len(groups)):
a = groups.get_group(site_a)['dwell-time']
p_val = stats.ttest_ind(a, baseline, equal_var = False).pvalue
if p_val < alpha:
print(' %i - : %f'
% (site_a, p_val))
, , - .
— 1- , 2- . , , - .
Github. .
, №4, , 1- 2- , 20 - .