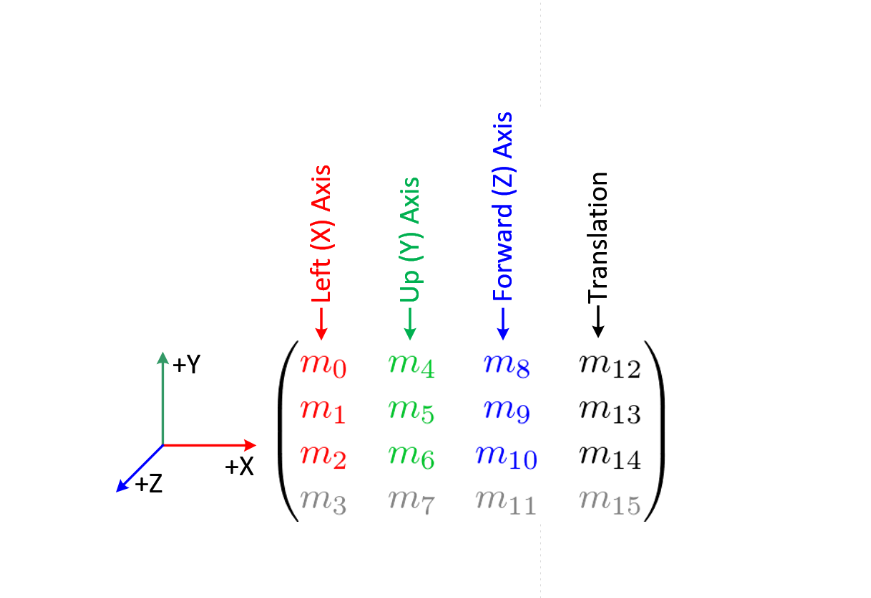
¿Por qué no una matriz de 3x3? ¿Por qué todo está organizado en una matriz de 4x4 exactamente así? ¿Por qué la última línea está llena de ceros y uno al final? Hice estas preguntas el día anterior, decidí investigar la pregunta y contar lo que descubrí.
En el artículo, solo nos interesarán las transformaciones afines y, en particular, la rotación, el escalado y el movimiento, que se utilizan activamente en la programación gráfica y el desarrollo de juegos en general.
: . , , , (A⋅x). , , , (+b).
T, x
, b x . x x', :
x ( ), b ( ).
, , . M, :
x' = 3x + 4 (3x +4 ) .
, ( 3x [3]), (x+4) , M x.
:
+4 +4y, y, x ,
2x2, x' = 3x+4 x, . . , .
2x2 , , - y, +4y , +4, x :
, , , , 3x+4 x' - y' y' ,
. : y' = 1 = 0 ⋅ x + 1 ⋅ 1
, x , .
(a), (b) (0 1) y' 1, x' , .
- , , . ():
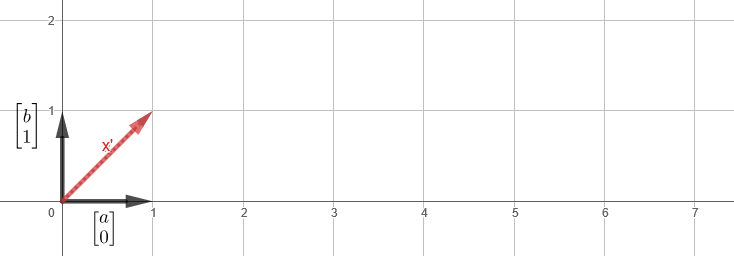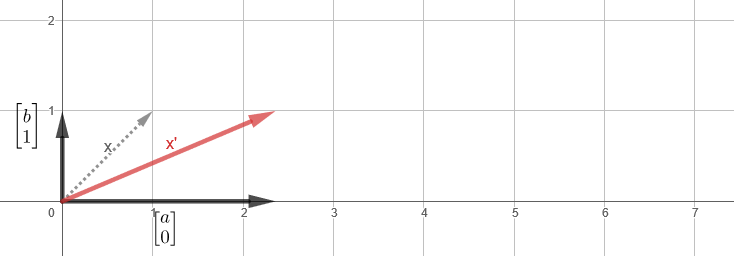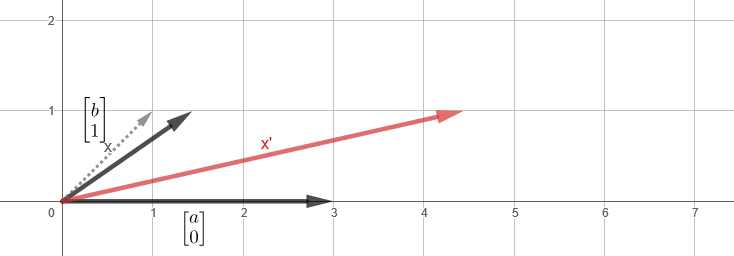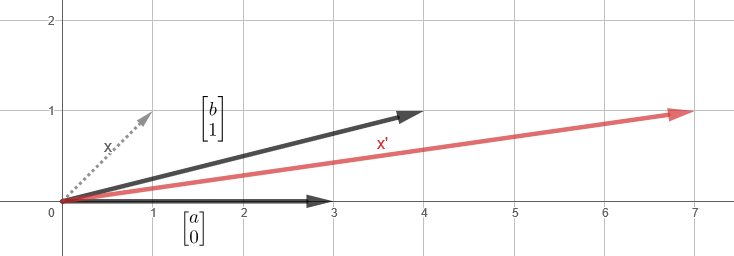
,

, , - z, y .

22 . b .
x' y' , , z' 1 .
, () , () :

:

Computing 2D affine transformations using only matrix multiplication
Brilliant. Linear Transformations
Explaining Homogeneous Coordinates & Projective Geometry
Nonlinear Transformation
Can non-linear transformations be represented as Transformation Matrices?
Linear transformations and matrices | Essence of linear algebra, chapter 3