¡Hola, Habr! Continuamos con el tutorial sobre la biblioteca opencv en python. Para aquellos que no han leído la primera parte, aquí: Parte 1 , y todos los demás: ¡lectura divertida!

Introducción
Ahora que está familiarizado con los conceptos básicos de esta biblioteca, es hora de comenzar las transformaciones básicas de las imágenes: cambio de tamaño, desplazamiento a lo largo de los ejes, recorte (recorte), rotación.
Cambio de tamaño de la imagen
, — . opencv resize():
def resizing():
res_img = cv2.resize(img, (500, 900), cv2.INTER_NEAREST), , — , , — (). — , . , , . , (cv2.INTER_NEAREST) , — . opencv : cv2.INTER_AREA, cv2.INTER_LINEAR( ), cv2.INTER_CUBIC cv2.INTER_LANCZOS4. cv2.INTER_AREA, — cv2.INTER_LINEAR. , , / , 1.5 , — . . :
res_img_nearest = cv2.resize(img, (int(w / 1.4), int(h / 1.4)),
cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
res_img_linear = cv2.resize(img, (int(w / 1.4), int(h / 1.4)),
cv2.INTER_LINEAR)— , — :
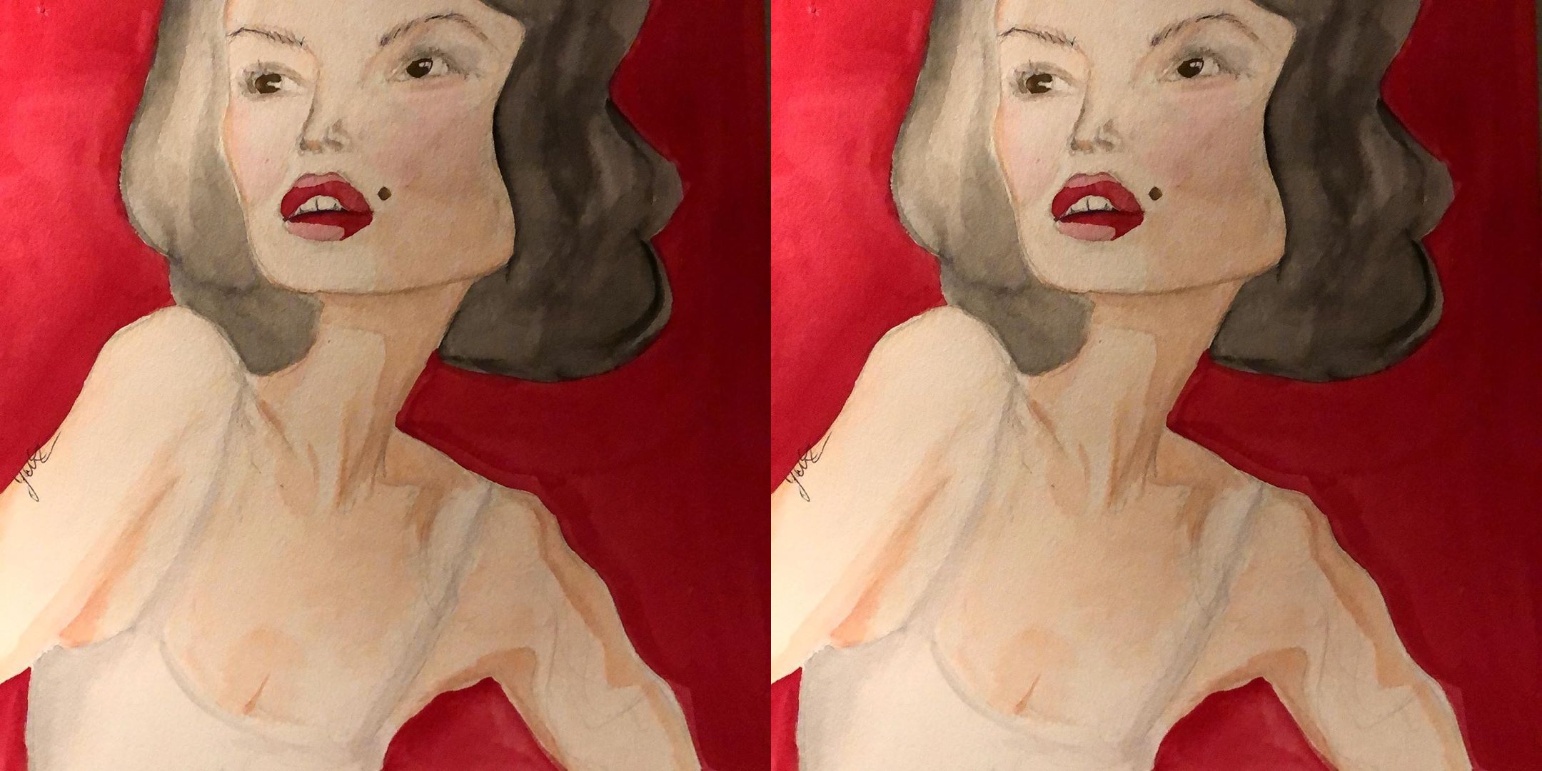

. — . , :
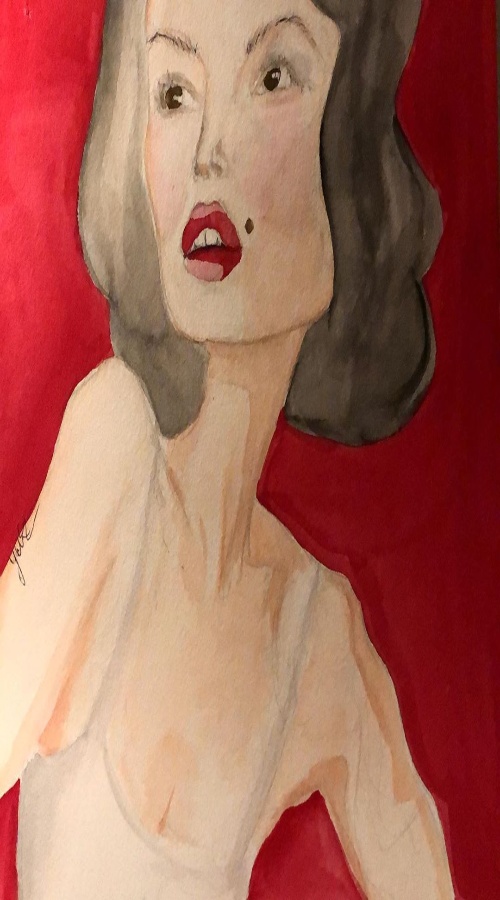

:
def resizing(new_width=None, new_height=None, interp=cv2.INTER_LINEAR):
h, w = img.shape[:2]
if new_width is None and new_height is None:
return img
if new_width is None:
ratio = new_height / h
dimension = (int(w * ratio), new_height)
else:
ratio = new_width / w
dimension = (new_width, int(h * ratio))
res_img = cv2.resize(img, dimension, interpolation=interp)ratio. , None, / /. , dimension cv2.resize().
cv2.warpAffine() , , :
def shifting():
h, w = img.shape[:2]
translation_matrix = np.float32([[1, 0, 200], [0, 1, 300]])
dst = cv2.warpAffine(img, translation_matrix, (w, h))
cv2.imshow(', ', dst)
cv2.waitKey(0), translation_matrix :
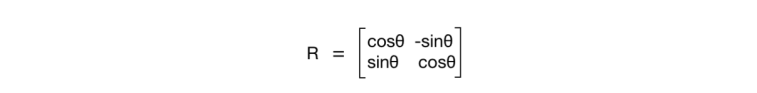
— [1, 0, tx ], tx — , . tx , — .
— [ 0, 1, ty], ty — , . ty , — . , .
, , , cv2.warpAffine(), , — , — . , :
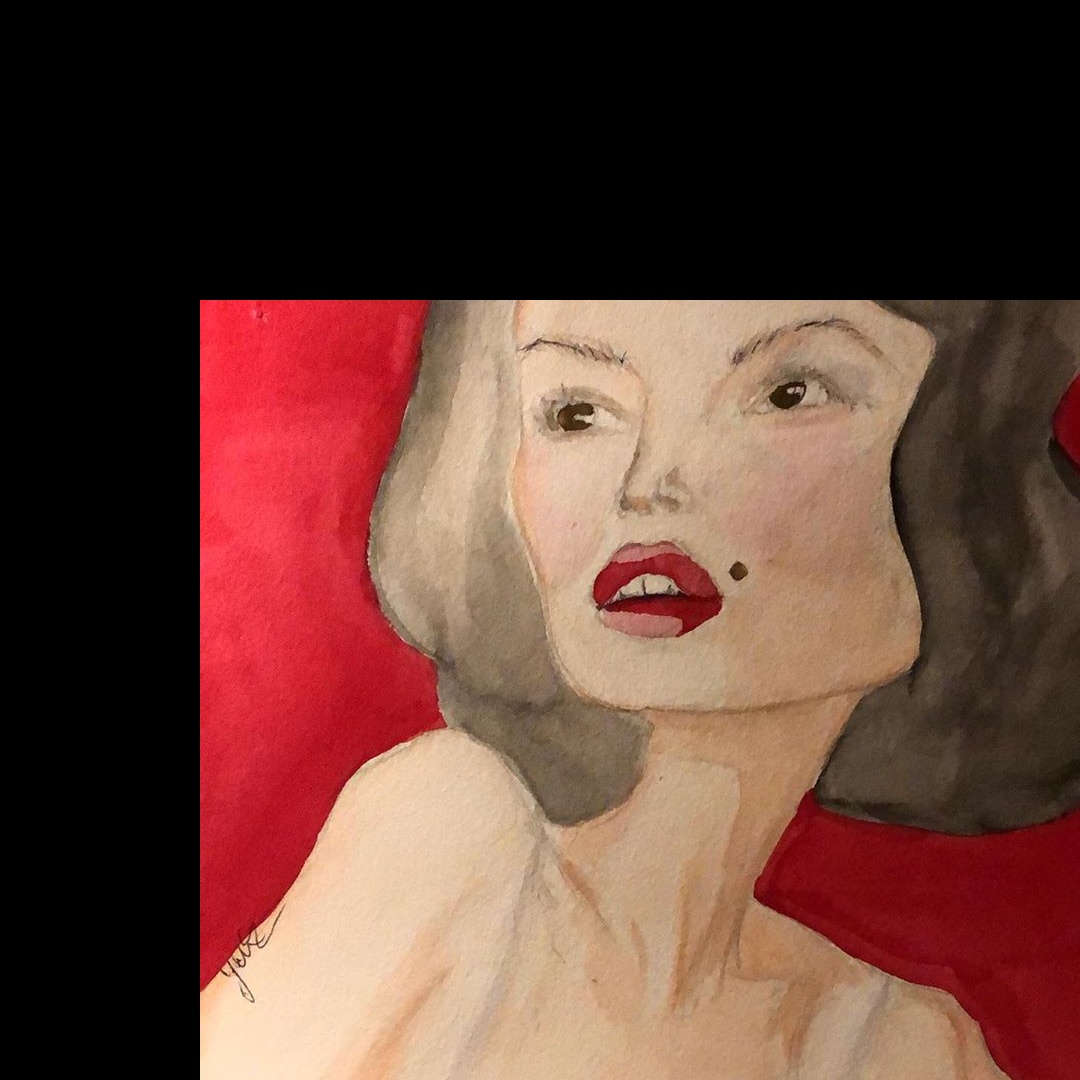

, , :
def cropping():
crop_img = img[10:450, 300:750]numpy , (300, 10) (750, 450), 10 — y, 300 — x, 450 — y 750 — x. , , :
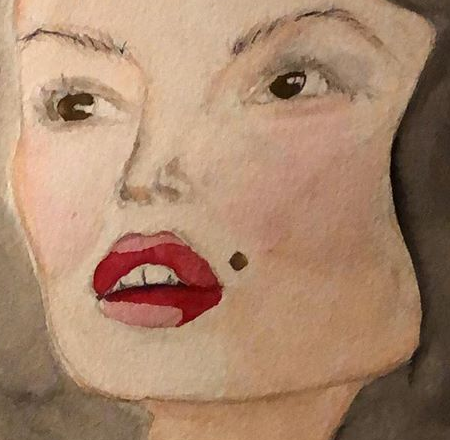

, , — :
def rotation():
(h, w) = img.shape[:2]
center = (int(w / 2), int(h / 2))
rotation_matrix = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, -45, 0.6)
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(img, rotation_matrix, (w, h)), , , cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(). , opencv , . , , — . 0.6, 40%, , . numpy, cv2.warpAffine(). , :

Ahora que la segunda parte ha llegado a su fin, el código fuente está disponible en github . ¡Gracias por su atención! ¡Te veo pronto!